We break down business functions into small services, provide them through endpoints, so that they are consumed by other applications across the enterprise or from third parties depending on the use cases. Microservices advocate to loosely integrate applications with high fault tolerance as well as great agility of development. With cloud technologies, AWS extends to serverless implementation that helps customers focus on the business logic part without managing servers. Events, a change in state or an update, are produced, ingested, and routed among the serverless services. This is the core concept of Event-Driven Architecture.
In this post, we are going to build REST
APIs using a part of those cloud services. The business logic is implemented
with Lambda, the data is stored in DynamoDB, and the APIs are deployed on API
Gateway.
Note: "Traffic that is in an Availability
Zone, or between Availability Zones in all Regions, routes over the AWS private
global network."
We are about to create a REST API to create
a table in DynamoDB.
Table: Music
Partition Key: Artist
Sort Key: SongTitle
Attribute: AlbumTitle
Let’s start with creating the backend Lambda function.
Create a Backend Lambda Function
Sign in the Management Console, open Lambda
Console, click Functions on the left navigation pane. A list of functions in
the Region associated with your account will be presented on the page.
Click Create Function.
Choose Author from scratch.
Under Basic information, enter
DemoCreateTable for Function name, choose Python 3.12 for Runtime.
For Permissions, check Use an
existing role, select TestRoleLambda for Existing role.
TestRoleLambda is a role created with AmazonDynamoDBFullAccess
policy attached.
Click Create function.
The function is created, and we can view
its details.
Click Code tab. You’ll see the
default function which returns a message, “Hello from Lambda!”.
Replace the default function with the
following source codes.
Lambda: DemoCreateTable
import jsonimport boto3 as boimport botocore as bcdef lambda_handler(event, context):if event['headers'] is not None:dictparam = event['headers']elif event['queryStringParameters'] is not None:dictparam = event['queryStringParameters']elif event['body'] is not None:dictparam = json.loads(event['body'])else:return {'statusCode': 400,'body': json.dumps('Name of the table to be created is not specified.')}try:tablename = dictparam['table']client = bo.client('dynamodb')response = client.create_table(AttributeDefinitions=[{'AttributeName': 'Artist','AttributeType': 'S',},{'AttributeName': 'SongTitle','AttributeType': 'S',},],KeySchema=[{'AttributeName': 'Artist','KeyType': 'HASH',},{'AttributeName': 'SongTitle','KeyType': 'RANGE',},],ProvisionedThroughput={'ReadCapacityUnits': 5,'WriteCapacityUnits': 5,},TableName= tablename,)code = 200msg = 'Table created'except bc.exceptions.ClientError as e:code = 500msg = str(e)except KeyError as e:code = 400msg = 'KeyError exception happened while using key {} to get the table name.'.format(str(e))return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}
Click Deploy
How to Test the Lambda Function?
Go to Test tab, choose Create new event, enter DemoEventCreateTable for Event name, enter {“headers”:{“table”:”Music”}} for Event JSON, and click Save.
Go back to Code tab, click Test.
You can check the execution results. The response says the table has been
created.
After we created the Lambda function, it is
time to create the REST API now.
Navigate to the API Gateway Console, click
APIs on the left pane. You’ll see a list of currently available APIs.
Click Create API.
Choose REST API.
Choose New API.
Enter DemoRESTAPI for API name.
Choose Regional for API endpoint type.
Click Create API.
The Console navigates to the Resources
page.
Click Create resource.
Enter DemoResourceMusic for Resource
name.
Click Create resource.
DemoResourceMusic was created immediately
under root “/”. We are going to create one more resource under
DemoResourceMusic.
Click Create resource again.
Enter DemoResourceMusicTable for Resource
name.
Click Create resource.
You can find the newly created resource,
DemoResouceMusicTable, appearing in the Resources tree. We are going to create
a PUT method for it.
Click Create method.
Choose PUT for Method type.
Choose Lambda function for Integration
type.
Check Lambda proxy integration.
For Lambda function, choose
DemoCreateTable created in the previous step.
Click Create method.
A success message pops up on the top of
the page.
Test the API
We can run a test right now. How? Go to Test
tab, enter “table:Music” in the Headers box, and click Test on
the bottom of the page.
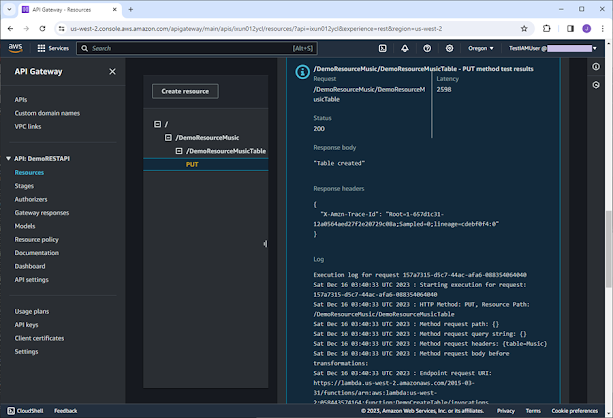
On the same page, we can view the results
as shown on the screenshot below. We got the message, “Table created”,
generated by the backend Lambda function.
To make the API available to the consumers,
we’ll need to deploy it first.
Click Deploy API.
Choose New
stage for Stage.
Enter Test for Stage
name.
Click Deploy.
So, the deployment was created and active
for test now.
We are going to dump logs to CloudWatch to
trace the API’s execution.
Click Logs and tracing.
Choose Full request and response logs for CloudWatch
logs.
Enable Custom access logging.
Create a Log group named by DemoRESTAPI in
the CloudWatch Console and paste its ARN in the field of Access log
destination ARN.
For Log format, get the JSON
template from “Learn more” link.
Click Save changes.
We also need to set up an IAM role for
outputting logs to CloudWatch.
Navigate to Settings of the API, go
to Logging section, and click Edit.
Choose TestRoleApiGateway, a predefined role assigned with policy AmazonAPIGatewayPushToCloudWatchLogs.
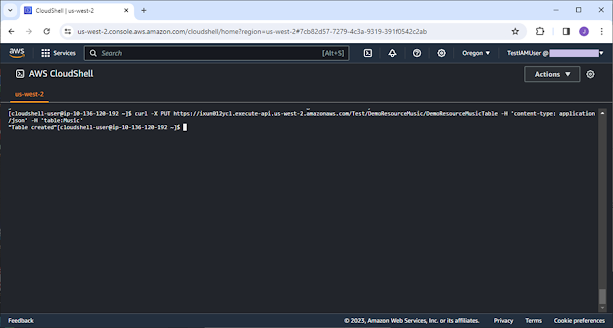
After all these are done, we can test the
REST API via CloudShell using curl command.
curl -X PUT https://ixun012ycl.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Test/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicTable -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'table:Music'
We got the table created message. It works
well.
Logs
Let’s check the logs and get an insight into what actually
happened inside the API.
Open CloudWatch Console, click Log groups
on the left pane, and we can identify the following log groups associated with
the REST API.
- API-Gateway-Exection-Logs_ixun012ycl/Test
- DemoRESTAPI
The below are examples of them, respectively.
What Is Passed to the Backend Lambda?
This varies depending on enabling or disabling Lambda proxy integration
setting.
In case of enabling Lambda proxy
integration, the Request with the full-scale contents is handed to the backend
function, as shown below.
{'resource': '/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicTable','path': '/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicTable','httpMethod': 'PUT','headers': {'table': 'Music'},'multiValueHeaders': {'table': ['Music']},'queryStringParameters': None,'multiValueQueryStringParameters': None,'pathParameters': None,'stageVariables': None,'requestContext': {'resourceId': 'fby8li','resourcePath': '/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicTable','httpMethod': 'PUT','extendedRequestId': 'QBkk2FGJvHcFt3g=','requestTime': '16/Dec/2023:07:13:34 +0000','path': '/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicTable','accountId': 'nnnnnnnnnnnn','protocol': 'HTTP/1.1','stage': 'test-invoke-stage','domainPrefix': 'testPrefix','requestTimeEpoch': 1702710814759,'requestId': 'ab5bfc95-cf93-4eac-8357-e4a1f75f8585','identity': {'cognitoIdentityPoolId': None,'cognitoIdentityId': None,'apiKey': 'test-invoke-api-key','principalOrgId': None,'cognitoAuthenticationType': None,'userArn': 'arn:aws:iam::nnnnnnnnnnnn:user/TestIAMUser','apiKeyId': 'test-invoke-api-key-id','userAgent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/120.0.0.0 Safari/537.36','accountId': 'nnnnnnnnnnnn','caller': 'AIDAQ3G4CFOKKZWQESTX4','sourceIp': 'test-invoke-source-ip','accessKey': 'ASIAQ3G4CFOKGRULRTC2','cognitoAuthenticationProvider': None,'user': 'AIDAQ3G4CFOKKZWQESTX4'},'domainName': 'testPrefix.testDomainName','apiId': 'ixun012ycl'},'body': None,'isBase64Encoded': False}
On the contrary, only the body of the
Request is passed to the backend function if Lambda proxy integration setting
is disabled.
Of course, the Responses are also slightly different. The Lambda function returns status code and body.
return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}
With Lambda proxy integration, the code is
set as the Response’s Status Code and the message is set as its body.
Status
200
Response body
"Table created"
Response headers
{
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-657d49e2-f5f6fd248da8e0881dd97df6;Sampled=0;lineage=cdebf0f4:0"
}
Without Lambda proxy integration, the
code and the message are combined and set as the Response’s body.
Status
200
Response body
{"statusCode": 200, "body": "\"Table created\""}
Response headers
{
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-65801497-1347f5f3c51608798c637128;Sampled=0;lineage=cdebf0f4:0"
}
Access Control
To manage access to a REST API, API Gateway
supports several mechanisms in place, please refer to Amazon API Gateway
Developer Guide for more information.
For Resource policy, you can define it in
the API Gateway Console. A Resource policy is stated in the IAM policy
language, here is a standard template of granting access to a list of source VPCs.
{"Version": "2012-10-17","Statement": [{"Effect": "Deny","Principal": "*","Action": "execute-api:Invoke","Resource": "execute-api:/{{stageNameOrWildcard}}/{{httpVerbOrWildcard}}/{{resourcePathOrWildcard}}","Condition": {"StringNotEquals": {"aws:sourceVpc": "{{vpcID}}"}}},{"Effect": "Allow","Principal": "*","Action": "execute-api:Invoke","Resource": "execute-api:/{{stageNameOrWildcard}}/{{httpVerbOrWildcard}}/{{resourcePathOrWildcard}}"}]}
More APIs
Following the procedures stated above, we
can build more methods, more APIs. For example, we create another method,
DELETE, for the resource DemoResourceMusicTable.
Lambda: DemoDeleteTable
import jsonimport boto3 as boimport botocore as bcdef lambda_handler(event, context):if event['headers'] is not None:dictparam = event['headers']elif event['queryStringParameters'] is not None:dictparam = event['queryStringParameters']elif event['body'] is not None:dictparam = json.loads(event['body'])else:return {'statusCode': 400,'body': json.dumps('Name of the table to be deleted is not specified.')}try:tablename = dictparam['table']client = bo.client('dynamodb')response = client.delete_table(TableName = tablename,)code = 200msg = 'Table deleted'except bc.exceptions.ClientError as e:code = 500msg = str(e)except KeyError as e:code = 400msg = 'KeyError exception happened while using key {} to get the table name.'.format(str(e))return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}
For the same resource, we don’t have to
create a separate Lambda function for each HTTP method, indeed, we can create
one Lambda function, and use httpMethod to separate processes for each method.
For DemoResourceMusicItem resource, a
consolidated function is prepared for the methods.
Lambda: DemoHandleItem
import jsonimport boto3 as boimport botocore as bcdef lambda_handler(event, context):if event['headers'] is not None:dictparam = event['headers']elif event['queryStringParameters'] is not None:dictparam = event['queryStringParameters']elif event['body'] is not None:dictparam = json.loads(event['body'])else:return {'statusCode': 400,'body': json.dumps('Item to be processed is not specified.')}## Add an itemif event['httpMethod'] == 'PUT':try:tablename = dictparam['table']artist = dictparam['artist']songtitle = dictparam['songtitle']albumtitle = dictparam['albumtitle']client = bo.client('dynamodb')response = client.put_item(Item={'Artist': {'S': artist,},'AlbumTitle': {'S': albumtitle,},'SongTitle': {'S': songtitle,},},ReturnConsumedCapacity='TOTAL',TableName = tablename,)code = 200msg = 'Item added'except bc.exceptions.ClientError as e:code = 500msg = str(e)except KeyError as e:code = 400msg = 'KeyError exception happened while using key {} to get the value.'.format(str(e))return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}## Delete an itemelif event['httpMethod'] == 'DELETE':try:tablename = dictparam['table']artist = dictparam['artist']songtitle = dictparam['songtitle']client = bo.client('dynamodb')response = client.delete_item(Key={'Artist': {'S': artist,},'SongTitle': {'S': songtitle,},},TableName = tablename,)code = 200msg = 'Item deleted'except bc.exceptions.ClientError as e:code = 500msg = str(e)except KeyError as e:code = 400msg = 'KeyError exception happened while using key {} to get the value.'.format(str(e))return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}## Select an itemelif event['httpMethod'] == 'GET':try:tablename = dictparam['table']artist = dictparam['artist']songtitle = dictparam['songtitle']client = bo.client('dynamodb')response = client.get_item(Key={'Artist': {'S': artist,},'SongTitle': {'S': songtitle,},},TableName = tablename,)code = 200if 'Item' in response.keys():msg = response['Item']else:msg = 'Item not found'except bc.exceptions.ClientError as e:code = 500msg = str(e)except KeyError as e:code = 400msg = 'KeyError exception happened while using key {} to get the value.'.format(str(e))return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}## Update an itemelif event['httpMethod'] == 'POST':try:tablename = dictparam['table']artist = dictparam['artist']songtitle = dictparam['songtitle']albumtitle = dictparam['albumtitle']client = bo.client('dynamodb')response = client.update_item(ExpressionAttributeNames={'#AT': 'AlbumTitle',},ExpressionAttributeValues={':t': {'S': albumtitle,},},Key={'Artist': {'S': artist,},'SongTitle': {'S': songtitle,},},ReturnValues = 'ALL_NEW',TableName = tablename,UpdateExpression='SET #AT = :t',)code = 200msg = 'Item updated'except bc.exceptions.ClientError as e:code = 500msg = str(e)except KeyError as e:code = 400msg = 'KeyError exception happened while using key {} to get the value.'.format(str(e))return {'statusCode': code,'body': json.dumps(msg)}## Undefined requestelse:return {'statusCode': 400,'body': json.dumps('Undefined request.')}
Let’s run a test using the following
commands.
Delete a table:
curl -X DELETE https://ixun012ycl.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Test/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicTable -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'table:Music'
Put an item:
curl -X PUT https://ixun012ycl.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Test/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicItem -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'table:Music' -H 'artist:No One You Know' -H 'albumtitle:Somewhat Famous' -H 'songtitle:Call Me Today'
Update an item:
curl -X POST https://ixun012ycl.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Test/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicItem -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'table:Music' -H 'artist:No One You Know' -H 'albumtitle: Louder Than Ever' -H 'songtitle:Call Me Today'
Get an item:
curl -X GET https://ixun012ycl.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Test/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicItem -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'table:Music' -H 'artist:No One You Know' -H 'songtitle:Call Me Today'
Delete an item:
curl -X DELETE https://ixun012ycl.execute-api.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/Test/DemoResourceMusic/DemoResourceMusicItem -H 'content-type: application/json' -H 'table:Music' -H 'artist:No One You Know' -H 'songtitle:Call Me Today'